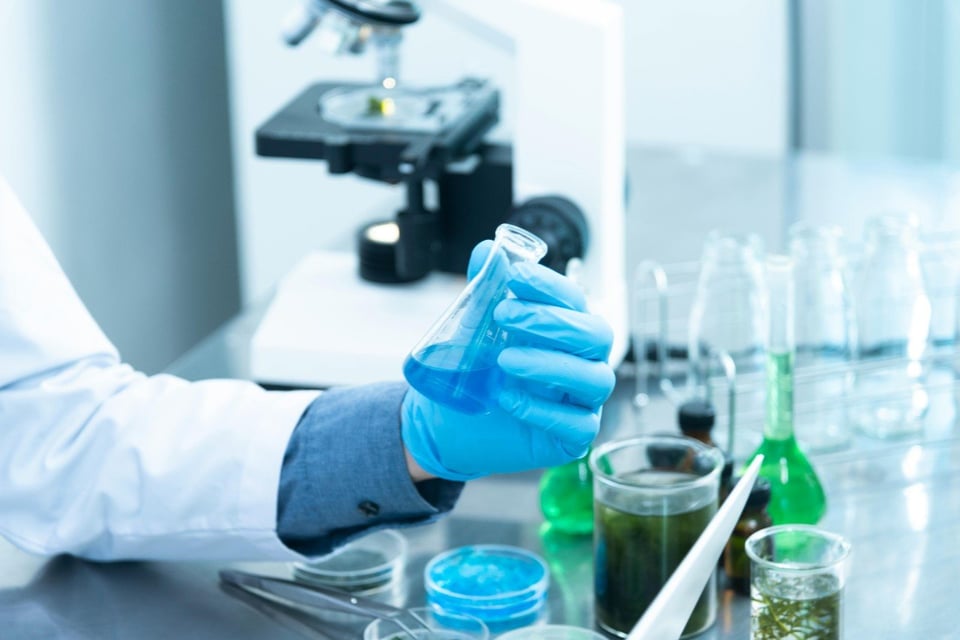

Biologics Characterization, CMC Analytical and Testing Services
Crystal Bio Solutions operates a 5,300 sq ft biologics characterization and CMC analytical lab in New Jersey that supports programs from discovery through clinical stages. We develop, validate and transfer various analytical methods for complex drug substances and drug products, deliver routine testing, execute stability studies and extended characterizations.
Identity, purity, potency, and safety testing using orthogonal biophysical and biochemical methods. Techniques include SEC, IEX, RP, HIC, CE-SDS, DLS, DSC, UV, fluorescence, and FTIR for structure and structure-function characterization.
Targeted assays for residuals and process impurities that affect product safety. Capabilities include host cell proteins and DNA, residual Protein A and detergents, residual solvents, endotoxin and bioburden. Results are delivered with clear acceptance criteria and trending.
Quantitative assays that link structure to function for PK and PD relevance. Options include cell-based potency, reporter and binding assays, and orthogonal readouts to confirm mechanism.
Modality-specific solutions for XDC conjugate, peptide, ASO, siRNA, mRNA, LNP and AAV, rapid method troubleshooting for complex matrices, method transfer in and out, and phase-appropriate studies.
 How Biologics Work and What Makes Them Unique
Biologics are therapies produced in living systems that act on specific molecular pathways and receptors. In autoimmune disease, for example, certain biologics modulate or block immune signals to reduce tissue damage. Unlike small molecules, biologics are large, structurally complex, and often heterogeneous. They are sensitive to heat and shear, prone to degradation or aggregation, and require tight controls to prevent microbial contamination. These properties make specialized analytics, storage, and handling essential across development and manufacturing.
How Biologics Work and What Makes Them Unique
Biologics are therapies produced in living systems that act on specific molecular pathways and receptors. In autoimmune disease, for example, certain biologics modulate or block immune signals to reduce tissue damage. Unlike small molecules, biologics are large, structurally complex, and often heterogeneous. They are sensitive to heat and shear, prone to degradation or aggregation, and require tight controls to prevent microbial contamination. These properties make specialized analytics, storage, and handling essential across development and manufacturing.
 How Biologics Are Approved by the FDA
In the United States, most biologics are reviewed by the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Sponsors open an IND to begin clinical studies, then progress through Phase 1 safety, Phase 2 dose and efficacy exploration, and Phase 3 confirmatory trials. Approval requires a Biologics License Application that integrates quality, nonclinical, and clinical evidence. Topics such as GMP compliance, comparability after process changes, device or combination product considerations, and pharmacovigilance plans are assessed before marketing authorization is granted.
How Biologics Are Approved by the FDA
In the United States, most biologics are reviewed by the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Sponsors open an IND to begin clinical studies, then progress through Phase 1 safety, Phase 2 dose and efficacy exploration, and Phase 3 confirmatory trials. Approval requires a Biologics License Application that integrates quality, nonclinical, and clinical evidence. Topics such as GMP compliance, comparability after process changes, device or combination product considerations, and pharmacovigilance plans are assessed before marketing authorization is granted.
.jpg?width=640&height=480&name=%E5%8C%BB%E7%96%97%E8%83%8C%E6%99%AF3D%E6%B8%B2%E6%9F%93%E7%A7%91%E6%8A%80%E6%84%9F%E5%9F%BA%E5%9B%A0%E7%BC%96%E8%BE%91%E8%8D%AF%E7%89%A9%E7%A0%94%E5%8F%91%E7%94%9F%E7%89%A9%E7%A7%91%E6%8A%80%E8%83%B6%E5%9B%8ADNA%E9%93%BE%E6%8F%92%E7%94%BB(%E5%95%86%E4%B8%9A%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8).jpg) Categories of Biologics and Their Applications
Categories of Biologics and Their Applications
- Recombinant proteins such as enzymes, hormones, and growth factors
- Monoclonal antibodies for autoimmune and oncology indications
- Bispecific and multispecific antibodies that engage multiple targets or cells
- Antibody-drug conjugates that deliver cytotoxic payloads with targeted specificity
- Fusion proteins and Fc-engineered formats designed for extended half-life or function
- Gene and cell therapies including using viral or non-viral delivery
- Oligonucleotide therapies such as siRNA and antisense
- mRNA vaccines and theraputics with LNP delivery



